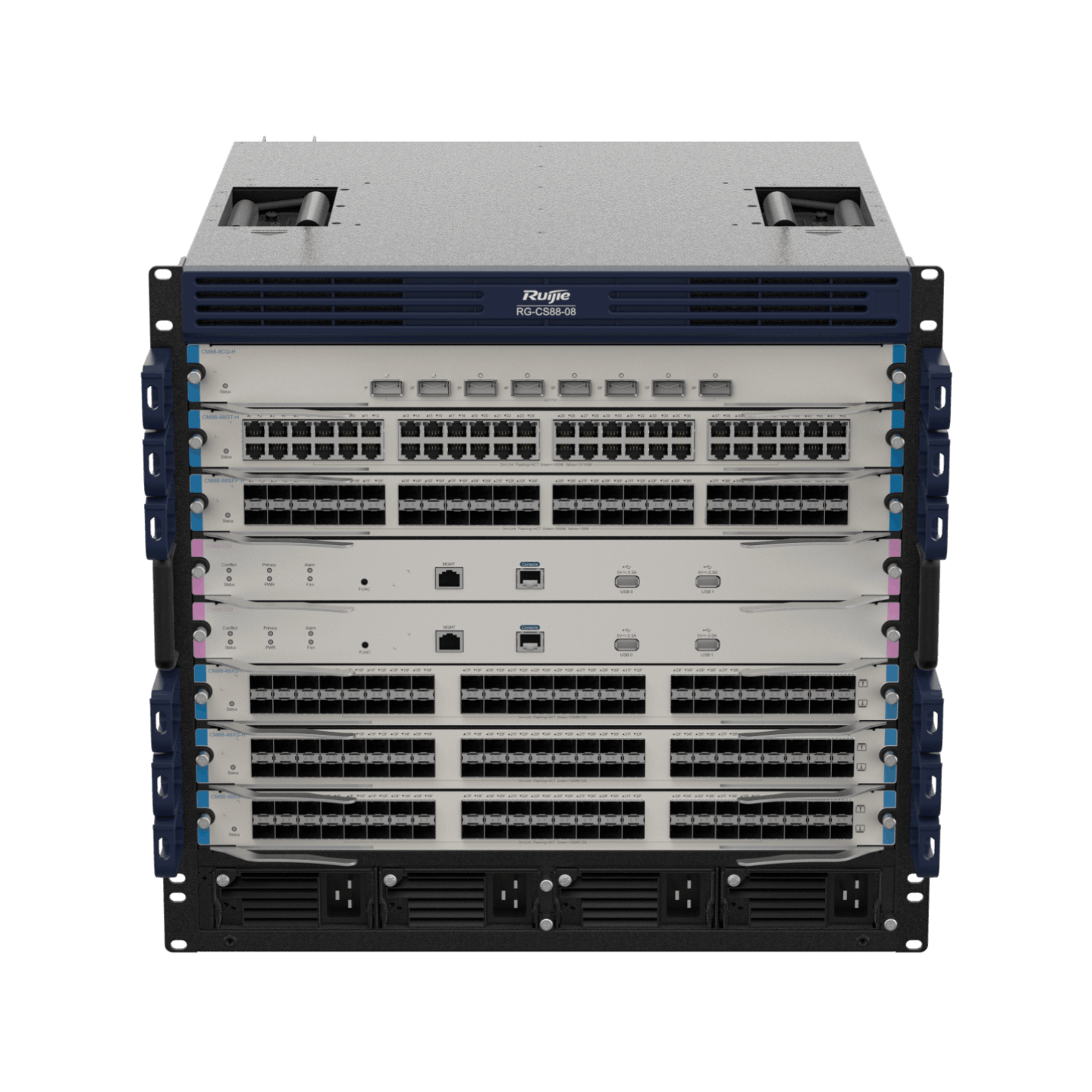
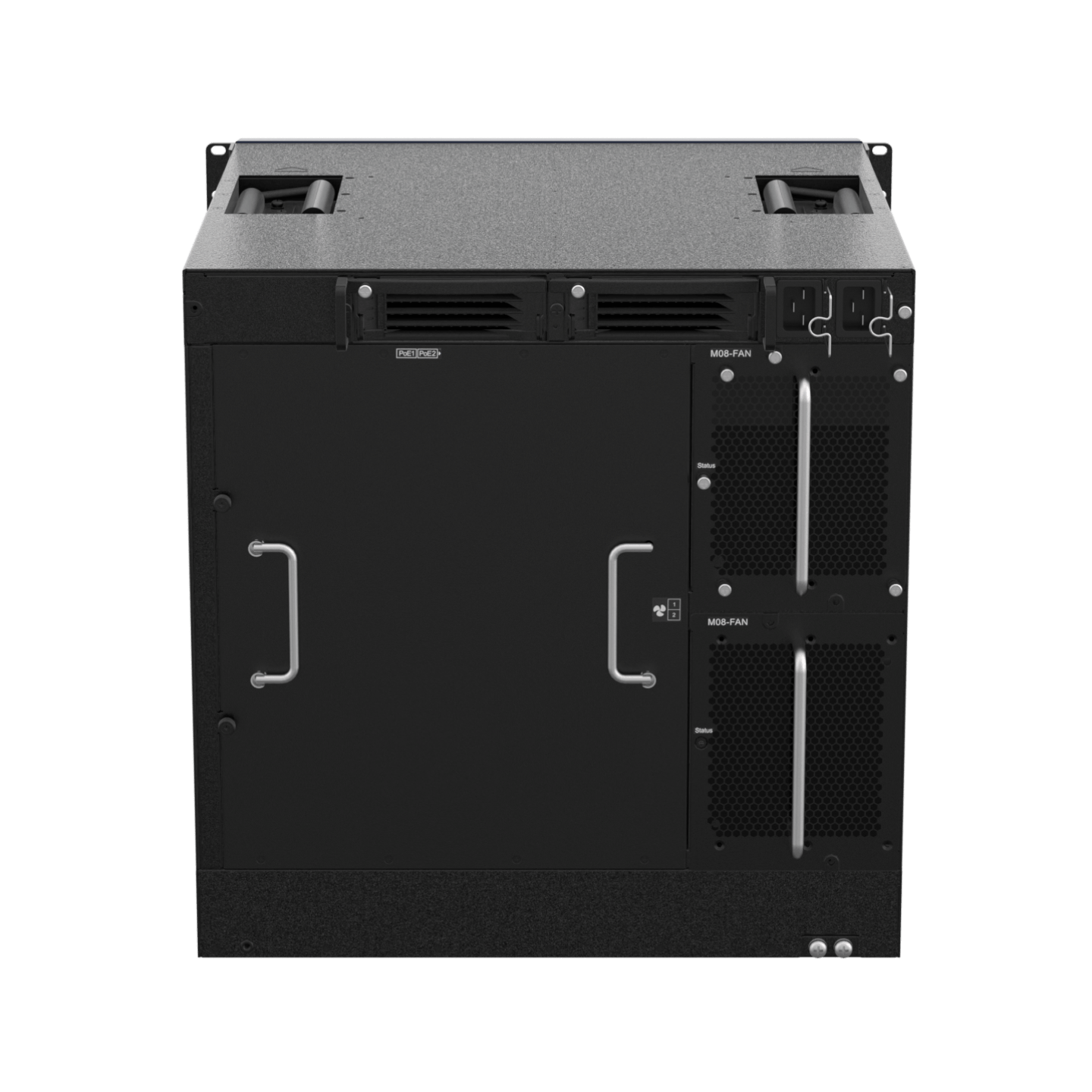
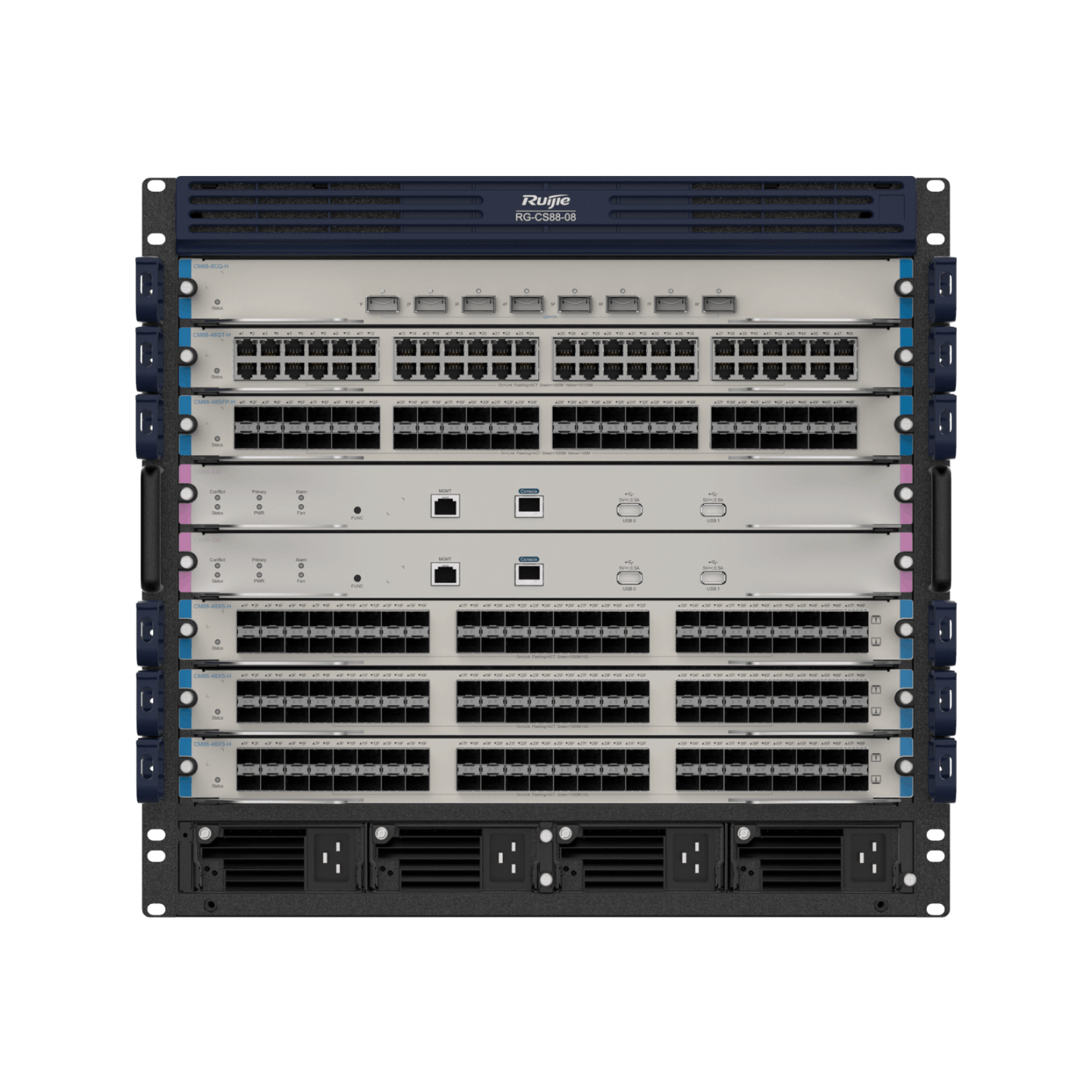
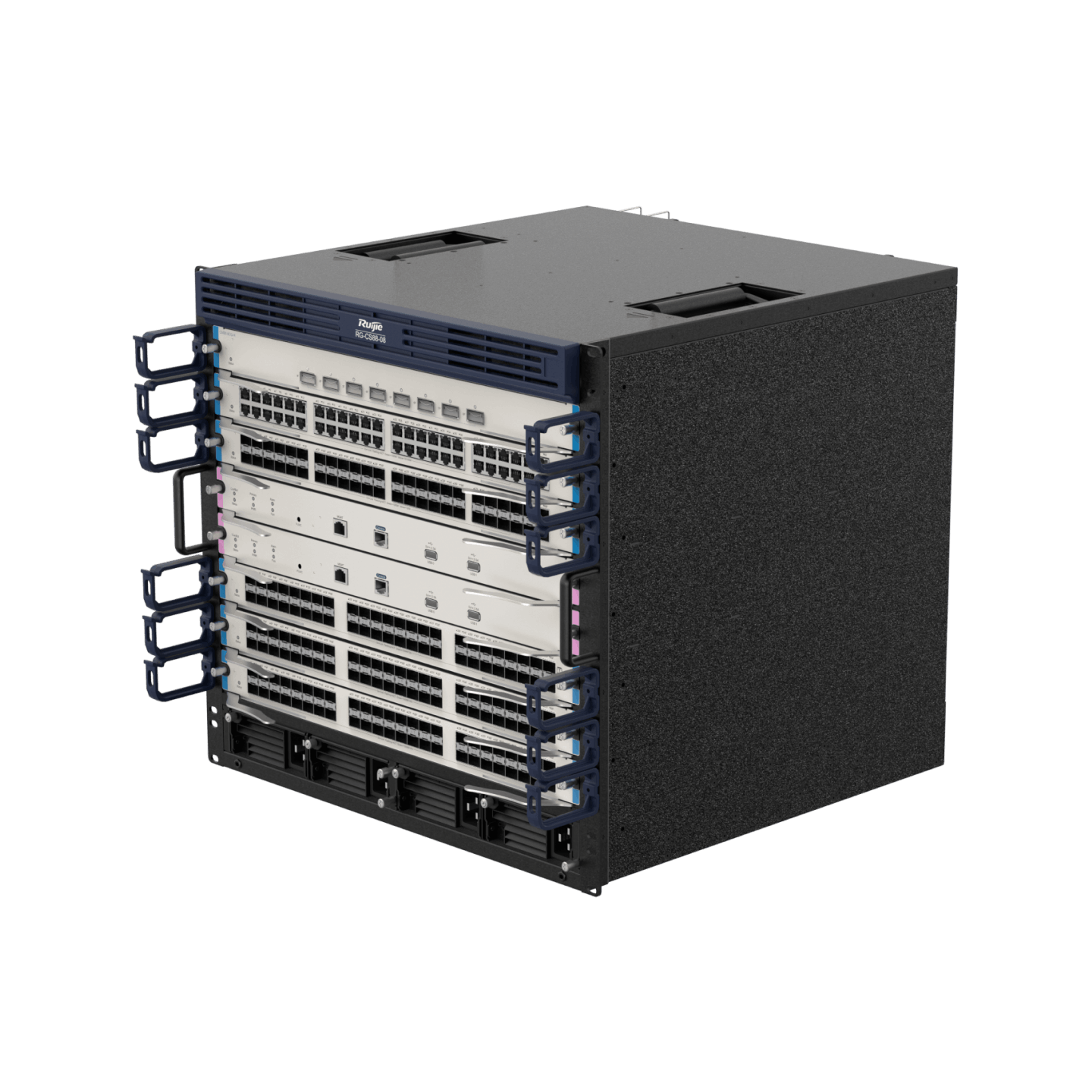
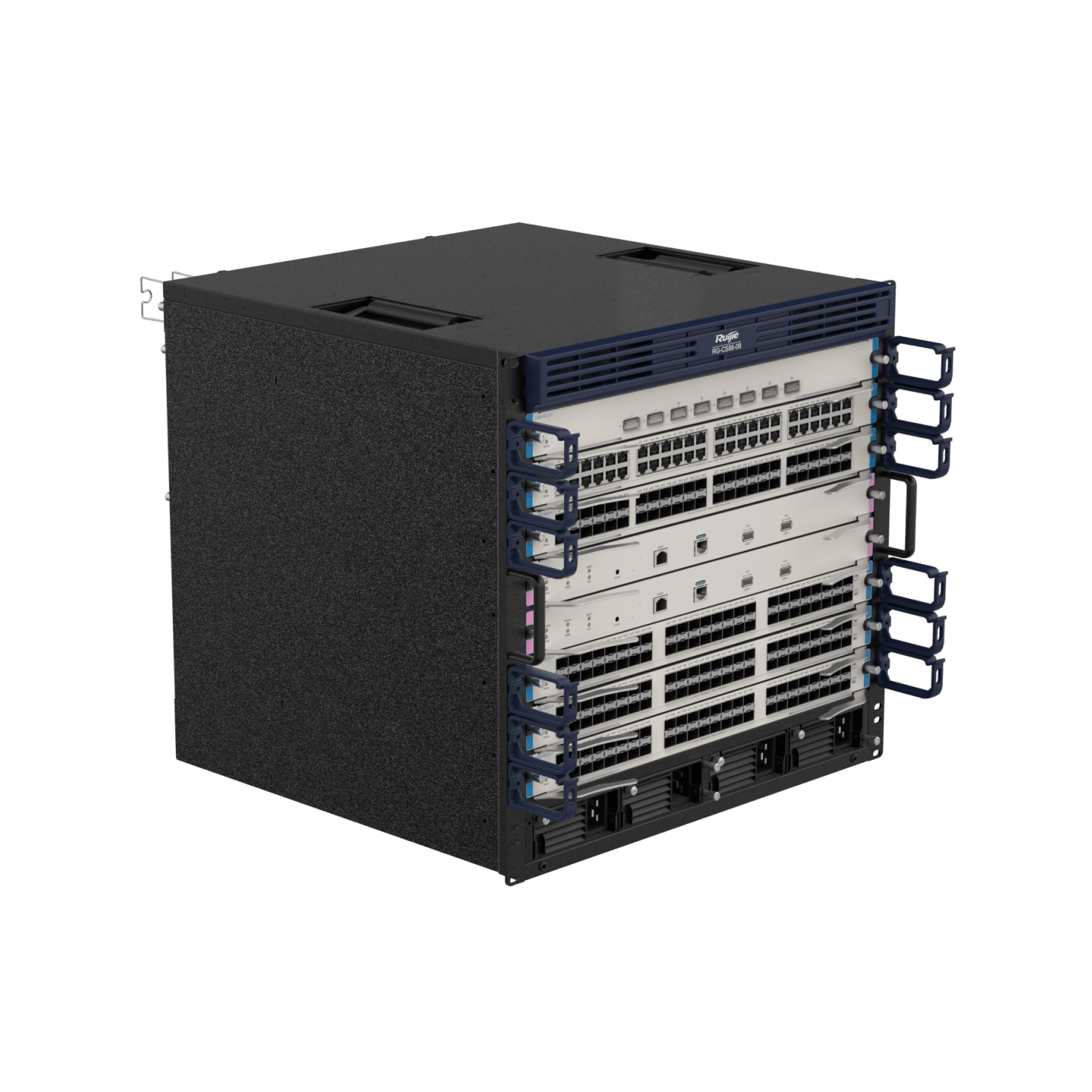
| RG-CS88 Series |
| Feature |
Description |
| Ethernet Switching |
Jumbo frame (maximum length: 9216 bytes) |
| 802.3az EEE |
| Maximum number of VLANs that can be created: 4,094 |
| Super VLAN, Private VLAN |
| MAC address-based, port-based, protocol-based, and IP subnet-based VLAN assignment |
| GVRP |
| Basic QinQ and selective QinQ |
| STP (IEEE 802.1.d), RSTP (IEEE 802.1w), and MSTP (IEEE 802.1s) |
| ERPS (G.8032) |
| LLDP/LLDP-MED |
| MPLS |
MPLS IPv6 |
| MPLS L3VPN |
| MPLS 6VPE |
| MPLS MIB (RFC 1273, RFC 4265, and RFC 4382) |
| IP Service |
Static and dynamic ARP |
| DHCP client |
| DHCP relay |
| DHCP server |
| DHCP snooping |
| DNS |
| DHCPv6 client, DHCPv6 relay, and DHCPv6 snooping |
| GRE tunnel |
| Manual tunnel, automatic tunnel, and ISATAP tunnel for IPv6 |
| Neighbor Discovery (ND) and ND snooping |
| IP Routing |
Static routing |
| RIP and RIPng |
| OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 |
| IPv4/IPv6 IS-IS |
| BGP4 and BGP4+ |
| IPv4/IPv6 VRF |
| Policy-based routing (PBR) |
| GR |
| EVPN |
| Multicast |
IGMP v1/v2/v3 |
| IGMP proxy |
| IGMP snooping v1/v2/v3 |
| IGMP fast leave |
| PIM-DM, PIM-SM, and PIM-SSM |
| PIM-SSM for IPv4 and IPv6 |
| MSDP to achieve inter-domain multicast |
| MLDv1 and MLDv2 |
| MLD v1/v2 snooping |
| Multicast static routing |
| Multicast source IP address check Multicast source port check |
| PIM-SMv6 |
| ACL and QoS |
Standard IP ACLs (hardware ACLs based on IP addresses) |
| Extended IP ACLs (hardware ACLs based on IP addresses or TCP/UDP port numbers) |
| Extended MAC ACLs (hardware ACLs based on source MAC addresses, destination MAC addresses, and optional Ethernet type) |
| Expert-level ACLs (hardware ACLs based on flexible combinations of the VLAN ID, Ethernet type, MAC address, IP address, TCP/UDP port number, protocol type, and time range) |
| ACL80 and IPv6 ACL |
| Applying ACLs globally (hardware ACLs based on flexible combinations of the VLAN ID, Ethernet type, MAC address, IP address, TCP/UDP port number, protocol type, and time range) |
| ACL redirection |
| Port traffic identification |
| Port traffic rate limiting |
| 802.1p |
| Traffic classification based on 802.1p priorities, DSCP priorities, and IP precedences |
| Congestion management: SP, WRR, DRR, WFQ, SP+WRR, SP+DRR, and SP+WFQ |
| Congestion avoidance: tail drop, RED, and WRED |
| CAR |
| Eight priority queues per port |
| Security |
AAA |
| RADIUS authorization and accounting |
| TACACS+ |
| Portal authentication, RADIUS, and TACACS+ login authentication |
| IEEE802.1X authentication, MAC address bypass (MAB) authentication, and interface-based and MAC address-based 802.1X authentication |
| Web authentication |
| Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) |
| SSHv1 and SSHv2 |
| Global IP-MAC binding |
| ICMP |
| Port security |
| IP source guard |
| DAI |
| SAVI |
| ARP spoofing prevention |
| CPU Protect Policy (CPP) and NFPP |
| Various attack defense functions, including NFPP and ARP anti-attack |
| uRPF |
| Login authentication and password security |
| Unknown multicast packets are not sent to the CPU, and unknown unicast packets can be suppressed. |
| Reliability |
Rapid Ethernet Uplink Protection (REUP) |
| Rapid Link Detection Protocol (RLDP), Layer 2 link connectivity detection, unidirectional link detection, and VLAN-based loop control |
| Data Link Detection Protocol (DLDP) |
| IPv4 VRRP v2/v3 and IPv6 VRRP |
| VRRP for the super-VLAN |
| BFD |
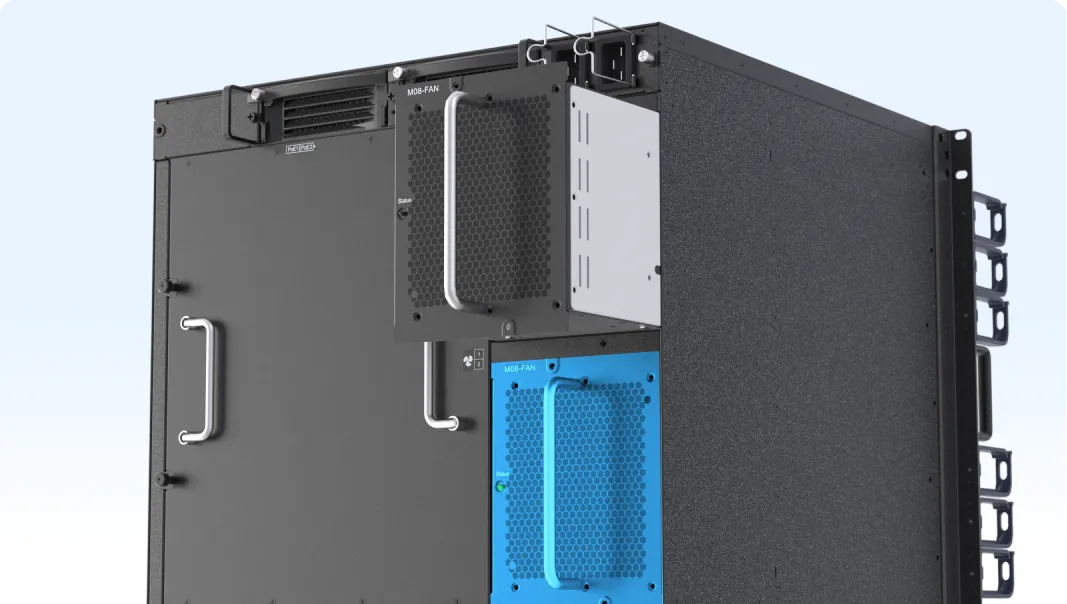
| 1+1 redundancy for supervisor modules and fan modules, and N+M redundancy for power modules |
| Hot swapping of components |
| Hot patch and online installation of patches |
| GR for OSPF/IS-IS/BGP |
| BFD for VRRP/OSPF/BGP4/ISIS/ISISv6/static routing |
| Device virtualization |
VSU |
| NMS and maintenance |
SPAN, RSPAN, and ERSPAN |
| sFLOW |
| NTP |
| SNTP |
| FTP and TFTP |
| SNMP v1/v2/v3 |
| RMON (1, 2, 3, 9) |
| NETCONF |
| CWMP |
| gRPC |
| Cloud and SON |
| Console/AUX Modem/Telnet/SSH2.0 CLI configuration |
| Fault alarm and auto-recovery |
| System operation logging |