| Hareware Specifications |
S7805C |
S7808C |
S7810C |
| Interface Specifications |
| Power module |
2 |
2 |
4 |
| Supervisor module slot |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| Line card slot |
3 |
6 |
8 |
| Switch fabric module slot |
Built-in |
2 (integrated with supervisor modules) |
4 (2 are integrated with supervisor modules) |
| System Specifications |
| Packet forwarding rate |
4,500 Mpps |
9,000 Mpps |
12,000 Mpps |
| System switching capacity |
6 Tbps |
12 Tbps |
16 Tbps |
| MAC address |
● Number of global MAC addresses EB card: 64,000 DA card: 96,000 (default) and 288,000 (max.) FA card: 80,000 FB card: 96,000 ● Number of static MAC addresses EB card: 4,000 DA card: 10,000 FA card: 4,000 ● FB card: 40,000 |
| ARP table |
EB card: 10,000 (default and recommended) DA card: underlay: 75,000; overlay: 0 (default and recommended) FA card: underlay: 30,000; overlay: 0 FB card: underlay: 50,000; overlay: 0 (default and recommended) |
| Number of IPv4 unicast routes |
EB card: 12,000 (default and recommended, shared with IPv6 routes) DA card: 12,000 (default and recommended, shared with IPv6 routes) FA card: 12,000 (default and recommended, shared with IPv6 routes) FB card: 134,000 (default and recommended, shared with IPv6 routes) |
| Number of IPv4 multicast routes |
EB card: 8,000 DA card: 16,000 FA card: 8,000 FB card: 16,000 |
| Number of IPv6 unicast routes |
EB card: 6,000 (shared with IPv4 routes) DA card: 6,000 (shared with IPv4 routes) FA card: 6,000 (shared with IPv4 routes) FB card: 50,000 (shared with IPv4 routes) |
| Number of IPv6 multicast routes |
EB card: 4,000 DA card: 8,000 FA card: 4,000 FB card: 8,000 |
| Number of ACEs |
● Ingress EB card: 3,500 DA card: 8,000 FA card: 5,000 FB card: 4,500 ● Egress EB card: 1,000 DA card: 1,000 FA card: 1,000 ● FB card: 2,000 |
| Number of VSU members |
2 |
2 |
2 |
| Dimensions and Weight |
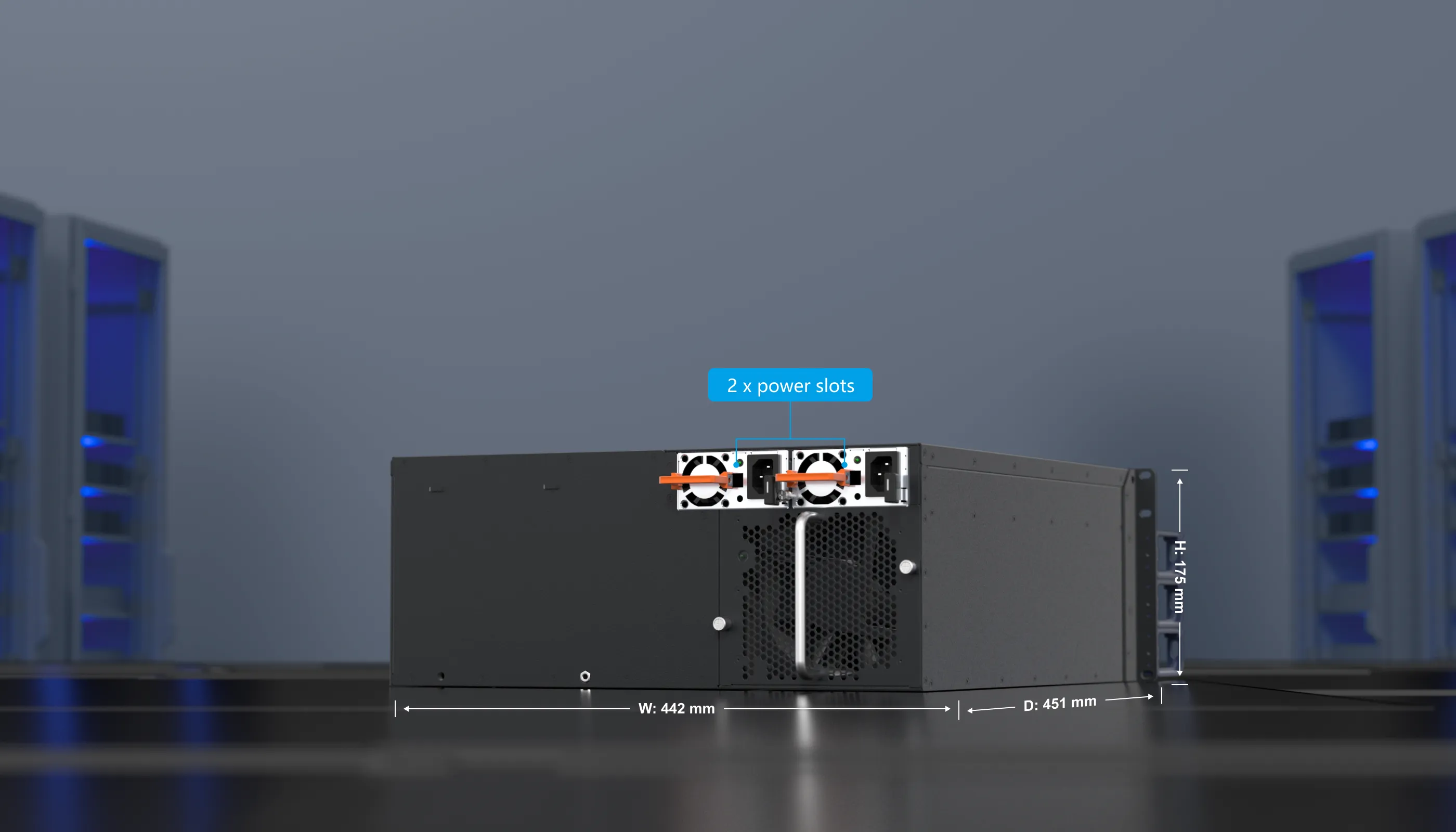
| Dimensions (W x D x H) |
442 mm x 451 mm x 175 mm (17.40 in. x 17.76 in. x 6.89 in., 4 RU) |
442 mm x 465mm x 441.7 mm (17.40 in. x 18.31 in. x 17.39 in., 10 RU) |
442.5 mm x 560 mm x 442 mm (17.42 in. x 22.05 in. x 17.40 in., 10 RU) |
| Weight (empty chassis and fan modules) |
32.35 kg (71.32 lbs) |
35.6 kg (78.48 lbs) |
43.6 kg (96.12 lbs) |
| CPU and Storage |
| CPU |
● Supervisor module M7805C-CM II: 1.5 GHz quad-core processor ● Service module EA/EB card: 1.0 GHz quad-core processor DA/F card: 1.5 GHz quad-core processor |
● Supervisor module M7808C-CM II: 1.5 GHz quad-core processor ● Service module EA/EB card: 1.0 GHz quad-core processor DA/F card: 1.5 GHz quad-core processor |
● Supervisor module M7808C-CM II: 1.5 GHz quad-core processor ● Service module EB card: 1.0 GHz quad-core processor DA/F card: 1.5 GHz quad-core processor ● Switch fabric module M7810C-FE-D I/M7810C-FE-F I: 1.5 GHz quad-core processor |
| Storage |
Flash memory M7805C-CM II: 1 GB EA card: 512 MB EB card: 512 MB DA/F card: 8 GB SDRAM M7805C-CM II: DDRIII 4 GB EA card: DDR3 1 GB EB card: DDRIII 1 GB DA card: DDR4 1 GB F card: DDR4 2 GB |
Flash memory Supervisor module: M7808C-CM II: 8 GB Service module: EA card: 512 MB EB card: 512 MB DA/F card: 8 GB SDRAM Supervisor module: M7808C-CM II: DDR4 4 GB Service module: EB card: DDR3 1 GB DA card: DDR4 1 GB F card: DDR4 2 GB |
Flash memory Supervisor module: M7810C-CM/M7810C-CM-F: 8 GB Service module: EB card: 512 MB DA/F card: 8 GB Switch fabric module: M7810C-FE-D I: 8 GB M7810C-FE-F I: 8 GB SDRAM Supervisor module: M7810C-CM/M7810C-CM-F: DDR4 4 GB Service module: EB card: DDR3 1 GB DA card: DDR4 1 GB F card: DDR4 2 GB Switch fabric module: M7810C-FE-D I card: DDR4 1 GB M7810C-FE-F I: DDR4 2 GB |
| Power and Consumption |
| Maximum power consumption |
Chassis RG-S7805C: < 80 W Supervisor module: M7805C-CM II: < 21 W Service module: M7800C-24SFP/12GT4XS-EB: < 85 W M7800C-48GT4XS-EB: < 70 W M7800C-48SFP4XS-EB: < 101 W M7800C-24GT24SFP4XS-EB: < 88 W M7800C-32XS4QXS-DA: < 210 W M7800C-48GT-FA: < 75 W M7800C-48SFP-FA: < 95 W M7800C-48XS-FB: < 160 W M7800C-8CQ-FB: < 130 W |
Chassis RG-S7808C: < 176 W Supervisor module: M7808C-CM II: < 50 W Service module: M7800C-24SFP/12GT4XS-EB: < 85 W M7800C-48GT4XS-EB: < 70 W M7800C-48SFP4XS-EB: < 101 W M7800C-24GT24SFP4XS-EB: < 88 W M7800C-32XS4QXS-DA: < 210 W M7800C-48GT-FA: < 75 W M7800C-48SFP-FA: < 95 W M7800C-48XS-FB: < 160 W M7800C-8CQ-FB: < 130 W |
Chassis RG-S7810C: < 432 W Supervisor module: M7810C-CM: < 50 W M7810C-CM-F: < 110 W Service module: M7800C-24SFP/12GT4XS-EB: < 85 W M7800C-48GT4XS-EB: < 70 W M7800C-48SFP4XS-EB: < 101 W M7800C-24GT24SFP4XS-EB: < 88 W M7800C-32XS4QXS-DA: < 210 W M7800C-48GT-FA: < 75 W M7800C-48SFP-FA: < 95 W M7800C-48XS-FB: < 160 W M7800C-8CQ-FB: < 130 W Switch fabric module: M7810C-FE-D I: < 50 W M7810C-FE-F I: < 105 W |
| Maximum output power |
● RG-PA300I-F: 90 V to 180 V; Power: 300 W 180 V to 264 V; Power: 300 W ● RG-PA460I-F: 90 V to 180 V; Power: 460 W 180 V to 264 V; Power: 460 W |
● RG-PA600I-F: 600 W ● RG-PA1600I-F: 90 V to 180 V: 12,00 W 180 V to 264 V: 1,600 W |
● RG-PA600I: 600 W ● RG-PA1600I: 90 V to 180 V: 1,200 W 180 V to 264 V: 1,600 W |
| Environment and Reliability |
| MTBF |
> 200,000 hours |
| Primary Airflow |
● Supervisor module Right-to-left airflow ● Service module Right-to-rear airflow ● System power module Built-in fan modules drawing air outward Front-to-rear airflow |
● Supervisor module /Service module Right-to-rear airflow ● System power module Front-to-rear airflow |
● Line card Side-to-rear airflow ● Supervisor module/FE Front-to-rear airflow |
| Operating temperature |
0°C to 50°C (32°F to 122°F) |
| Storage temperature |
–40°C to +70°C (–40°F to +158°F) |
| Operating humidity |
10% to 90% RH (non-condensing) |
| Storage humidity |
5% to 95% RH (non-condensing) |
| Operating altitude |
–500 m to +5,000 m (–1640.42 ft. to +16404.20 ft.) |
| Operating noise |
55.9 dB at the temperature of 35°C (95°F) 73.4 dB at the temperature of 50°C (122°F) |
| Interface surge protection |
All electrical ports support 4 kV surge protection in common mode or 1 kV surge protection in differential mode. |
Power port: 6 kV Telecom port: 4 kV (MGMT port) |